Nullish Coalescing Operator (??)
The nullish coalescing operator (??) is a logical operator that returns its right-hand side operand when its left-hand side operand is null or undefined, and otherwise returns its left-hand side operand.
Example:const username = null ?? 'suprabha';console.log(username);// suprabhaContents 📝
1. `&&` or `||` 2. Falsy Value 3. No chaining with `&&` or `||` operators 4. Browser Support 5. Reference
1️⃣ && or ||
As you know "&&" or "||" operators are used to handle ‘truthy’ and ‘falsy’ values.
2️⃣ Falsy Value
Falsy value in JavaScript:
- null
- undefined
- 0
- NaN
- false
- ""
"&&" or "||" operators work well with null or undefined values, but many false values can produce unexpected results.
Let's take an example, here we want to process the response where value is 0(zero). So when you get the response which is falsy, so it will return the right-hand side value. ➡️
const response = { count : 0}const count = response.count || 1;console.log(count) // 1To make it work, we will use nullish coalescing operator ??.
The nullish coalescing operator ?? acts very similar to the operator ||, except that it doesn’t use "truthy" when evaluating the operator. Instead, it uses the definition of “nullish,” which means that the value is strictly equal to null or undefined.
We will take the same example: 😎
const response = { count : 0}const count = response.count ?? 1;console.log(count) // 0Few Important Points:
With operator
Example:||if the first operand is truthy, it evaluates to the first operand. Otherwise, it evaluates to the second. With Nullish Coalescing operator, if the first operator is falsy but not nullish, it evaluates to the second operand.console.log(false || true);//trueconsole.log(false ?? true);//falsezerois evaluated as a falsy value; hence the expression evaluates to the right-hand value using the|| operator. But, with Nullish Coalescing operator, zero is not null. Therefore, the expression evaluates to the left-hand value.console.log(0 || 1); //1console.log(0 ?? 1); //0empty string
""is evaluated as a falsy value; hence the expression evaluates to the right-hand value using the|| operator. But, with Nullish Coalescing operator, empty string""is not null. Therefore, the expression evaluates to the left-hand value.console.log('' || 'supi!');//supiconsole.log('' ?? 'supi');//''If you check with the
undefinedornullit will be same:undefined || 10 // 10undefined ?? 10 // 10null || 100 // 100null ?? 100 // 100
Going to cover more example for better understanding:
const response = { settings: { nullValue: null, height: 400, animationDuration: 0, headerText: '', showSplashScreen: false }};
const undefinedValue = response.settings.undefinedValue ?? 'some other default'; // result: 'some other default'const nullValue = response.settings.nullValue ?? 'some other default'; // result: 'some other default'const headerText = response.settings.headerText ?? 'Hello, world!'; // result: ''const animationDuration = response.settings.animationDuration ?? 300; // result: 0const showSplashScreen = response.settings.showSplashScreen ?? true; // result: false3️⃣ No Chaining with AND or OR operators & │
It is not possible to combine both the AND (&&) and OR operators (||) directly with ??.
A SyntaxError will be thrown in such cases.
null || undefined ?? "supi"; // raises a SyntaxErrortrue || undefined ?? "supi"; // raises a SyntaxErrorHowever, providing parenthesis to explicitly indicate precedence is correct:
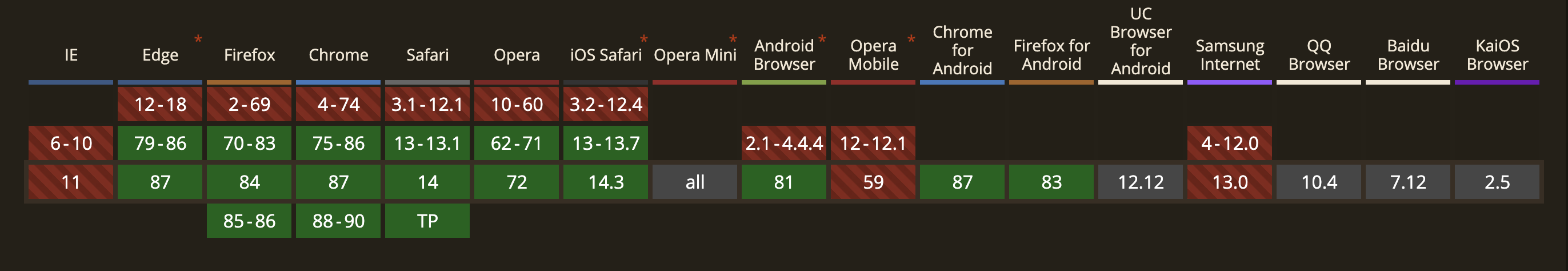
(null || undefined) ?? "supi"; // returns "supi"4️⃣ Browser Support 🖥
It works in recent versions of Chrome or Firefox, among others.
5️⃣ Reference 🧐
MDN Nullish coalescing operator
Summary ∑
- The operator
??has a very low precedence, a bit higher than?and=. - It’s forbidden to use it with
||or&&without explicit parentheses.
Thanks for reading the article ❤️
I hope you love the article. If you have any question, please feel free to ping me on @suprabhasupi 😋